By Princess Funsho Sumanu
The recent surge in cases of Mpox in Africa has prompted the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare it a global health emergency. With 2863 cases and 517 deaths reported, the situation is dire. However, in Nigeria, the Director-General of the Nigeria Center for Disease Control, Mr. Jide Idris, has reported only 39 cases and no deaths.
Mpox is a viral zoonotic disease caused by the monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus. While primarily found in central and western Africa, recent outbreaks have raised concerns about its potential spread beyond these regions. The disease shares symptoms with smallpox but is generally less severe.
The virus is transmitted to humans through contact with infected animals, such as rodents and primates. Human-to-human transmission can also occur through close physical contact with an infected individual’s skin lesions, respiratory secretions, or bodily fluids.
Educating the public about the disease and its implications is crucial to combat the spread of Mpox. In this article, we will discuss the causes of Mpox, the consequences of the outbreak, and the preventive measures individuals can take to protect themselves and their communities.
This can happen through direct contact, such as touching the sores or scabs of an infected person, respiratory droplets, or Inhaling droplets during prolonged face-to-face interaction. Contaminated Materials, use of clothing, bedding, or other items that have come into contact with an infected person can also spread the disease.
It’s essential to recognise that many early cases linked to the recent outbreak have been observed among populations engaged in close-contact activities, including intimate relations. The symptoms of Mpox typically begin 5 to 21 days after exposure and may include:
– Fever
– Headaches and muscle pains
– Swollen lymph nodes
– Fatigue
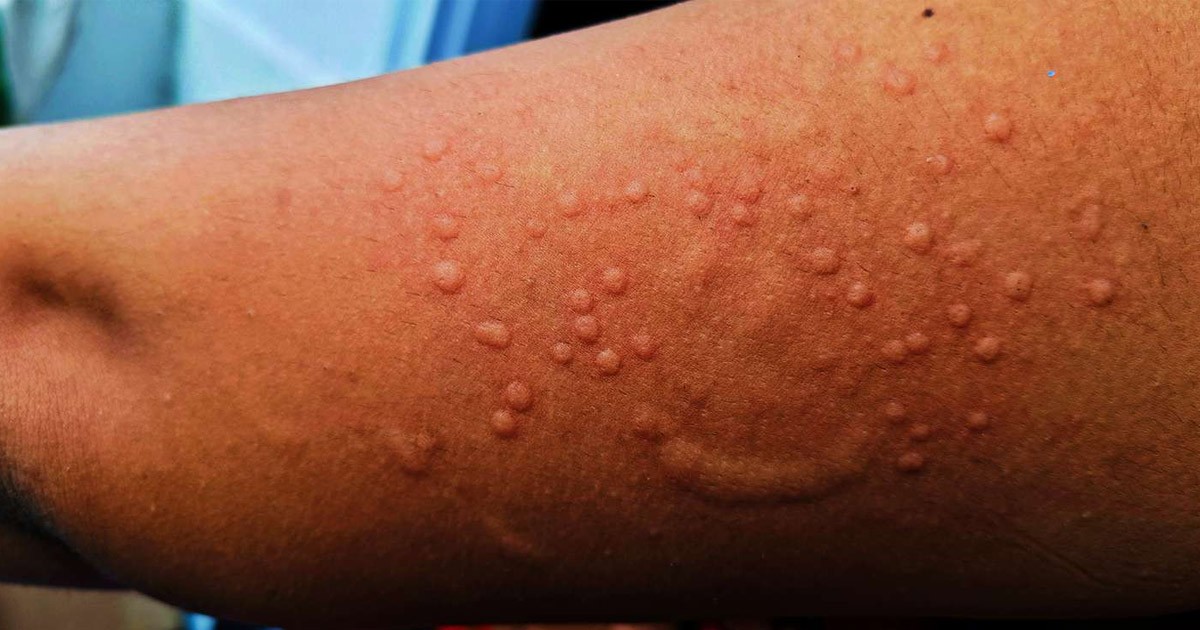
– Rash that evolves into fluid-filled blisters and eventually scabs
While Mpox can lead to severe illness, particularly in young children, pregnant women, and individuals with compromised immune systems, the overall fatality rate is relatively low compared to other viral infections in the same family.
As part of the ongoing preventive Measures efforts by the Nigerian government, the DG of the NCDC, Mr Jide Idris, said it has intensified surveillance across Nigeria to detect and respond to new cases swiftly. Also, states such as Lagos, Abuja, Enugu, Kano, Rivers, Cross River, Akwa Ibom, Adamawa, and Taraba have been placed on high alert to mitigate the spread of Mpox. It is, therefore, crucial to follow safety protocols and adopt preventive measures, including practising good hygiene, such as regular handwashing with soap and water or using hand sanitisers, which can help reduce the likelihood of transmission.
Avoiding close contact and limiting physical contact with individuals who are symptomatic or have been diagnosed with monkeypox and maintaining a safe distance is essential, especially in crowded settings. If you must be around someone infected, wearing a mask and other personal protective equipment (PPE) can provide an additional layer of safety.
Use of protective gear: If you care for a person with monkeypox or are coming into contact with potentially contaminated materials, gloves and masks are advisable.
Isolate Infected Individuals diagnosed with monkeypox should be isolated from others until they are no longer contagious, typically until all lesions have healed and new skin has formed.
Vaccination: While there is currently no specific vaccine for monkeypox, vaccination against smallpox effectively prevents monkeypox infection. In an outbreak, public health authorities may recommend vaccination for at-risk populations.
Educate yourself and others to understand the signs and symptoms of monkeypox, which can help in early detection and treatment. Share information with friends, family, and community members to promote awareness and preparedness.
The recent outbreak of monkeypox serves as a critical reminder of how infectious diseases can cross from animals to humans and spread within populations. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures related to monkeypox, individuals and communities can take responsible actions to protect their health. Staying informed and vigilant is critical in the face of potential outbreaks, ensuring we all play our part in safeguarding public health.
Princess Funsho Sumanu writes from the Ministry of Finance, Budget and Economic Planning.